Picture this: you’re cruising down the highway, enjoying the open road, when suddenly your vehicle starts to sputter and lose power. Panic sets in as you realize the culprit might be lurking right under your hood, hidden in plain sight – the fuel filter. This seemingly small component plays a crucial role in maintaining your vehicle’s performance and protecting your engine. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of fuel filters, shedding light on their importance, types, functions, and how does a fuel filter work, as well as how to properly maintain them to ensure a smooth and reliable ride.
Jump To
Short Summary
- Fuel filters are essential components that protect a vehicle’s engine fuel system from damage and promote optimal combustion.
- Regular inspection and replacement of fuel filters can help extend engine life by reducing the need for maintenance.
- When choosing a fuel filter, consider compatibility with your vehicle’s make/model, filter material & micron rating, brand & price.
The Role of Fuel Filters in Vehicle Performance
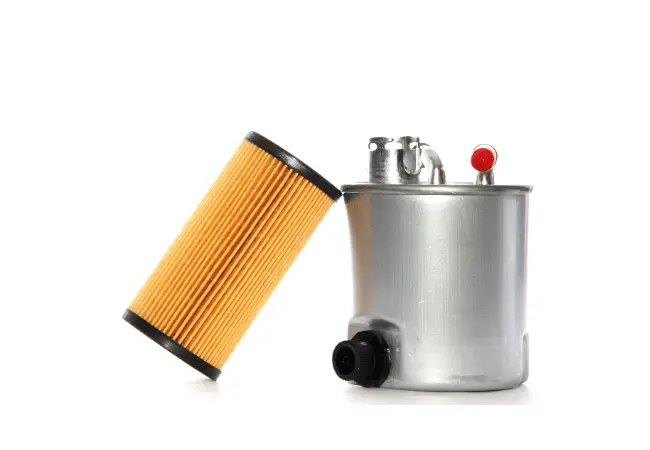

Fuel filters are the unsung heroes of your vehicle’s fuel system. They work tirelessly to remove impurities and contaminants from the fuel tank, and the fuel line to prevent unfiltered fuel from reaching the engine. These impurities include rust, paint chips, soot, dirt, sand, and even microbial growths that accumulate during fuel storage and transportation.
By keeping the fuel clean, fuel filters play a vital role in preventing engine damage, ensuring optimal combustion, and extending the life of a fuel injector in a vehicle’s fuel delivery system.
Preventing Engine Damage
A clogged fuel filter can spell disaster for your engine. When the filter is blocked, the fuel pump has to work harder, and the engine runs with a leaner fuel mixture, resulting in reduced power output.
Besides affecting fuel efficiency, particulate matter in the fuel injection system can be abrasive. This can lead to wear and tear on engine components. By regularly replacing the fuel filter, you can prevent such particles from reaching the fuel injectors, ensuring that your engine remains in tip-top condition.
Ensuring Optimal Combustion
Clean fuel is essential for achieving optimal combustion in your engine. Fuel filters eliminate impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine, ensuring that the fuel-air mixture is free of contaminants. Contaminated fuel can negatively impact engine performance, as it prevents fuel from burning efficiently, leading to decreased power output and increased emissions.
In the case of diesel engines, water in the fuel can cause friction, reduced lubricity, and potential overheating, emphasizing the importance of a reliable diesel fuel filter.
Extending Engine Life
By protecting the engine from potentially damaging particulates and debris, fuel filters not only improve performance and fuel efficiency but also reduce the need for maintenance over the lifetime of the vehicle.
Primary fuel filters, in particular, play a crucial role in safeguarding the fuel pump from damage or wear by filtering out larger debris, water, and wax.
Types of Fuel Filters and Their Functions
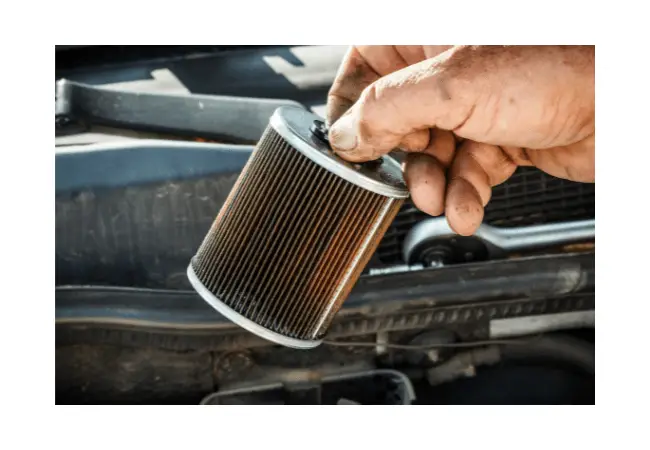

Fuel filters come in various shapes and sizes, each designed to cater to different types of engines and fuel systems.
In this section, we will explore the different types of fuel filters available for gasoline and diesel engines, as well as the differences between in-line and in-tank fuel filters that work well.
Gasoline Filters
Gasoline filters are designed to filter out impurities from gasoline to protect the fuel system and engine. There are two main types of gasoline filters: metal spin-on filters and ECO cartridge filters. Metal spin-on filters attach to the vehicle via threaded mounting, while ECO cartridge filters contain the filtration media and other components without the outer shell.
ECO cartridge filters are considered more environmentally friendly, as they have fewer metal or plastic parts that would otherwise be discarded.
Diesel Filters
Diesel filters, specifically designed for diesel engines, protect the diesel engine’s fuel system by removing water and contaminants. These filters need to be changed every 10,000 to 25,000 miles, depending on the vehicle’s usage and operating conditions.
Diesel filters are available in various types, such as ceramic filters, metal filters, and pleated paper filters, each designed to cater to different engine requirements.
In-Line vs. In-Tank Filters
In-line fuel filters are installed externally on the engine bay or fuel line, making them more accessible for maintenance and replacement. In contrast, in-tank fuel filters are mounted inside the gas tank, making them more challenging to access and service.
However, in-tank filters are designed to accommodate the specific environment of varying fuel types, providing efficient filtration in their respective conditions.
Fuel Filter Components and Mechanisms
Fuel filter components include filter media, which is responsible for trapping contaminants, inlet and outlet ports that facilitate the flow of fuel, and in the case of diesel filters, a water separation mechanism that removes water from diesel fuel.
In this section, we will delve deeper into these components to understand how they work together to keep your engine running smoothly.
Filter Media
Filter media are available in two primary types: natural and synthetic. Synthetic filter media, primarily composed of glass fibers, are capable of screening out finer particles, providing enhanced engine protection. However, synthetic media have a shorter lifespan and can cause additional stress on the fuel pump, leading to potential damage.
On the other hand, cellulose filter media, composed of plant fiber, offers minimal resistance to fuel flow and has a longer service life due to its resistance to clogging. However, its larger pores make it less effective in trapping very small particles.
Inlet and Outlet Ports
Inlet and outlet ports are openings in the fuel filter that facilitate the entry and exit of fuel. These ports are connected to the fuel lines, allowing fuel to flow through the filter media and be purified before reaching the engine.
Water Separation (Diesel Filters)
Water separation is a crucial process in diesel fuel filters. These filters feature a bowl at the bottom that collects water separated from the fuel. A drain valve enables the water bowl to be emptied when needed. This ensures the bowl is kept clean and hygienic.
Additionally, a water sensor provides a dashboard warning when the water level in the bowl reaches a critical point, signaling the need for draining.
Identifying and Addressing Fuel Filter Issues
Clogged or damaged fuel filters can reduce engine performance, increase emissions, and wear. It is essential to regularly check and assess your fuel filter to identify potential issues and address them before they escalate into costly repairs or replacements.
Regular maintenance of your fuel filter is key to ensuring your engine runs smoothly and efficiently. Inspecting the filter for signs of wear or damage can help you identify any potential problems before they become problems.
Symptoms of a Clogged or Damaged Fuel Filter
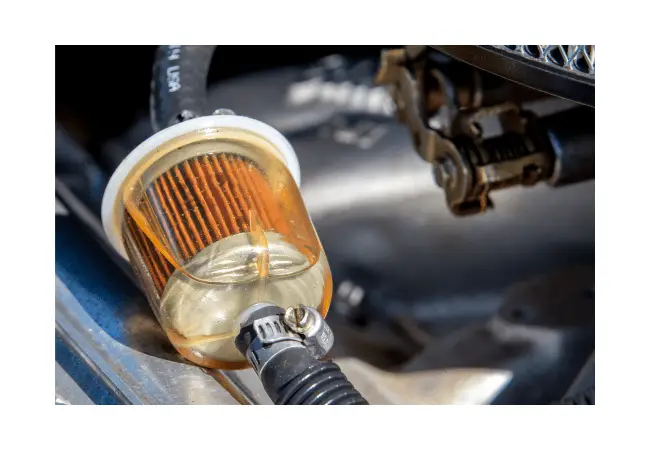

Common symptoms indicating a clogged or damaged fuel filter include decreased power output, engine misfires, stalling, and difficulty starting.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s time to take a closer look at your fuel filter and determine whether it requires cleaning or replacement.
Checking and Assessing Your Fuel Filter
To check and assess the condition of your fuel filter, you can inspect the filter media, measure fuel pressure, or monitor fuel flow when the engine is running.
This will help you determine if the filter is clogged or damaged and decide on the best course of action to rectify the issue.
Replacement vs. Cleaning
When dealing with a clogged or damaged fuel filter, you have two options: replace it or clean it. The choice depends on the type of filter media and the severity of the problem. Metal mesh filters can be cleaned and reused, while paper or nylon filters should be replaced.
Ultimately, the decision should be based on what is best for your engine’s performance and longevity.
Fuel Filter Replacement Process
Replacing a fuel filter can be a relatively straightforward task if done correctly. This process involves gathering the necessary tools and protective gear, relieving pressure in the fuel system, securing the vehicle, running the engine, switching off the engine, removing the old filter, and installing the new one.
In the following sections, we will discuss these steps in detail.
Tools and Precautions
Before embarking on the fuel filter replacement process, it’s essential to gather the necessary tools and protective gear, such as screwdrivers, open-end wrenches, a rag, a bowl for fuel spill containment, and safety equipment like goggles and gloves.
Additionally, ensure you work in a well-ventilated area and keep any items that may produce sparks or flames away from the workspace.
Removing the Old Fuel Filter
To remove the old fuel filter, start by depressurizing the whole fuel injection system by removing the fuel pump fuse from the vehicle’s fuse box, stabilizing the vehicle with a jack and jack stands, and running the engine for a few minutes.
After the engine is turned off, remove the fuel lines connected to the filter and unscrew the filter from its mounting bracket.
Installing the New Fuel Filter
Installing the new fuel filter involves connecting the fuel lines to the new filter and securing it to the mounting bracket. After the installation of the diesel filter is complete, reconnect the negative terminal of the car battery, start the engine, and run it for a few minutes to ensure proper fuel flow.
Finally, check the fuel tank for any fuel leaks around the new filter to confirm it has been installed correctly.
Choosing the Right Fuel Filter for Your Vehicle
Selecting the right fuel filter for your vehicle is crucial to ensure optimal engine performance and longevity. In this section, we will discuss the factors to consider when choosing a fuel filter, including compatibility with your vehicle’s make and model, filter material, micron rating, and price and brand considerations.
Compatibility with Vehicle Make and Model
It is essential to verify that the fuel filter is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model to ensure proper fit and efficient operation of modern cars.
Additionally, consider the type of fuel used by your vehicle, as gasoline fuel filters and diesel fuel filters have distinct designs and should not be interchanged.
Filter Material and Micron Rating
The filter material and micron rating play a significant role in determining the efficiency of a fuel filter. A lower micron rating indicates that the filter is more effective in trapping contaminants.
When selecting a fuel filter, consider the type of fuel, type of engine, and operating environment to determine the most suitable filter material and micron rating for your vehicle.
Price and Brand Considerations
When selecting a fuel filter based on price and brand, consider the quality of the product, its features, and its online and offline reputation. Keep in mind that while a cheaper fuel filter may save you money upfront, it could cost you more in the long run due to reduced performance and the need for more frequent replacements.
It is important to do your research and read reviews before making a purchase. Look for fuel filters that have been tested and certified by a reputable organization. Make sure the filter is compatible with your vehicle and meets the manufacturer’s specifications.
Summary
In conclusion, fuel filters play a vital role in maintaining your vehicle’s performance, protecting your engine, and extending its life. By understanding the different types of fuel filters, their components, and how to identify and address potential issues, you can ensure a smooth and reliable ride. Choosing the right fuel filter for your vehicle involves considering factors such as compatibility, filter material, micron rating, and price. Armed with this knowledge, you are now better equipped to make informed decisions about your vehicle’s fuel filter and keep your engine running at its best.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does fuel flow through a filter?
Fuel is pulled through the filter, with the vacuum created by the fuel pump. This suction forces the fuel up and out through the outlet side of the filter, after passing through the filtering medium.
This movement of fuel through a filter ensures any impurities are trapped, allowing clean fuel to flow to your engine.
What is the symptoms of a bad fuel filter?
The symptoms of a bad fuel filter include sputtering, hesitating, and stalling engines, as well as a poor engine performance, acceleration and fuel efficiency. If you notice any of these issues, it’s best to have your fuel filter replaced as soon as possible.
Replacing the fuel filter can help restore your engine’s performance and fuel efficiency, and can help prevent further damage to your engine.
How does a fuel filter work in a car?
A fuel filter in a car works by trapping dirt and debris before it enters the engine, preventing damage that would be caused by these particles. In addition, fuel filters help keep the engine running at peak efficiency by removing excess sediment from the fuel.
This ensures that your car runs smoothly with fewer issues.
What happens if you drive without a fuel filter?
If you drive without a fuel filter, dirt and debris will enter your engine’s fuel system, potentially clogging it up and causing severe damage. Your car’s performance will suffer as it struggles to get clean fuel to the engine.
So, in conclusion, driving without a fuel filter is not recommended.


1 thought on “How Does a Fuel Filter Work? A Comprehensive Guide”
Comments are closed.